Minimum Flips in Binary Tree to Get Result
You are given the root of a binary tree with the following properties:
- Leaf nodes have either the value
0or1, representingfalseandtruerespectively. - Non-leaf nodes have either the value
2,3,4, or5, representing the boolean operationsOR,AND,XOR, andNOT, respectively.
You are also given a boolean result, which is the desired result of the evaluation of the root node.
The evaluation of a node is as follows:
- If the node is a leaf node, the evaluation is the value of the node, i.e.
trueorfalse. - Otherwise, evaluate the node's children and apply the boolean operation of its value with the children's evaluations.
In one operation, you can flip a leaf node, which causes a false node to become true, and a true node to become false.
Return the minimum number of operations that need to be performed such that the evaluation of root yields result. It can be shown that there is always a way to achieve result.
A leaf node is a node that has zero children.
Note: NOT nodes have either a left child or a right child, but other non-leaf nodes have both a left child and a right child.
Example 1:
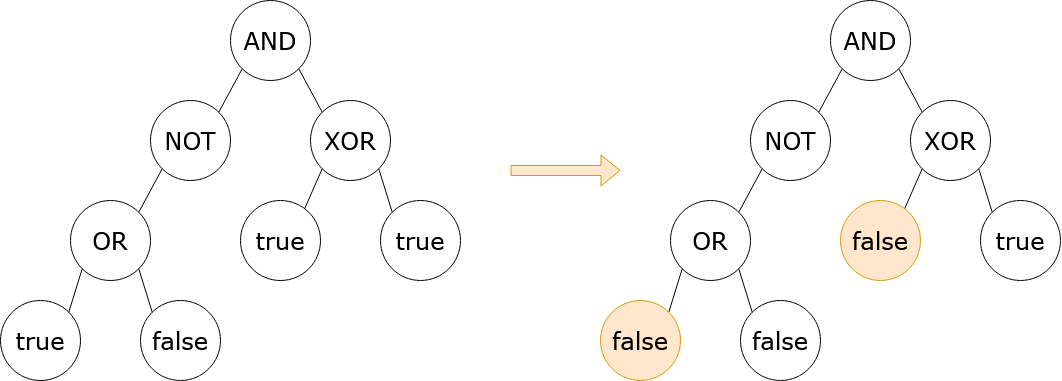
Input: root = [3,5,4,2,null,1,1,1,0], result = true Output: 2 Explanation: It can be shown that a minimum of 2 nodes have to be flipped to make the root of the tree evaluate to true. One way to achieve this is shown in the diagram above.
Example 2:
Input: root = [0], result = false Output: 0 Explanation: The root of the tree already evaluates to false, so 0 nodes have to be flipped.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 0 <= Node.val <= 5OR,AND, andXORnodes have2children.NOTnodes have1child.- Leaf nodes have a value of
0or1. - Non-leaf nodes have a value of
2,3,4, or5.